Transactional 애노테이션과 Rollback
in Spring on Spring Boot
@Transactional과 rollback의 관계
문제의 코드
@Transactional
public void attemptPasswordAuth(String email, String inputPassword) {
//... 생략
if (!passwordEncoder.matches(inputPassword, account.getPassword())) {
account.increaseLoginFailureCount();
adminAccountRepository.save(account);
throw new AdminAccountPasswordNotMatchedException();
}
//... 생략
}
위의 로직은 로그인시 비밀번호가 일치하지 않을 경우 login_fail_count를 +1 하는 로직이다.
물론 처음 코드를 봤을 때 발견하지 못했지만 위 코드는 로직상의 문제가 있다.
오늘은 위와 같이 코드를 작성했을 때 어떤 문제가 발생하며, 어떻게 해결해야 하는지도 알아보자!
Checked & Unchecked Exception
우선 Checked와 Unchecked의 특징을 리마인드 해보자.
[ ▾ Checked ]
- 예외처리가 필수이며, 처리하지 않으면 컴파일이 되지 않는다.
- Runtime Exception외 모든 예외
- Rollback이 되지 않고, 트랜잭션이 commit 까지 완료된다.
[ ▾ Unchecked ]
- 컴파일 때 체크되지 않고, Runtime에 발생하는 예외
- 에러 처리를 강제하지 않는다.
- Runtime Exception 하위의 모든 예외
- Rollback이 된다.
@Transactional과 rollback
우선 결론을 정리하자면 아래와 같다.
- @Transactional + throw Unchecked Exception = Roll Back
- @Transactional + try-catch Unchecked Exception = Commit
- @Transactional + throw Checked Exception = Commit
내부 동작원리
⒈ TransactionInterceptor.invoke() 메소드 호출
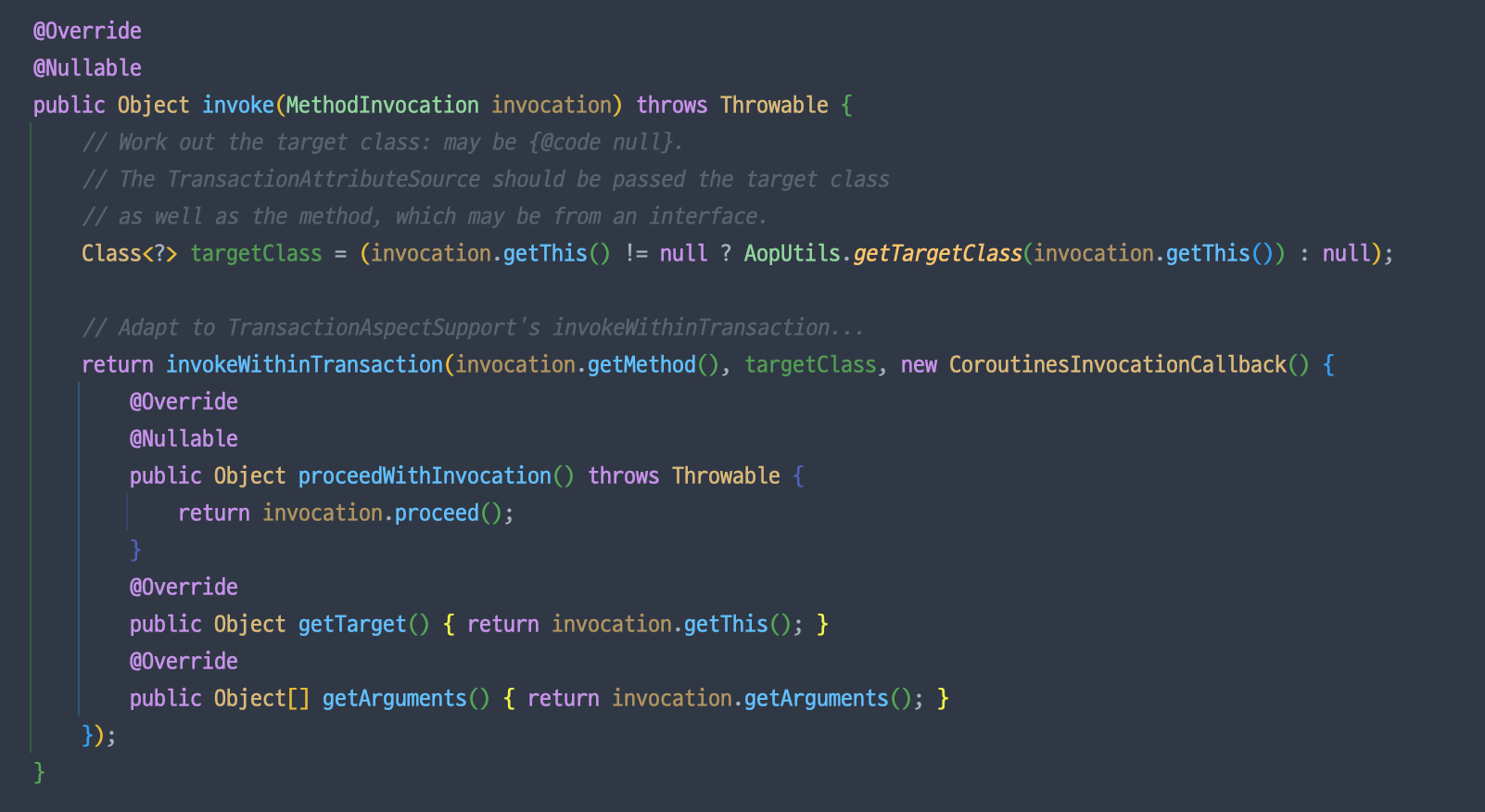
⒉ TransactionAspectSupport.invokeWithinTransaction(...) 메서드 진입
@Nullable
protected Object invokeWithinTransaction(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass,
final InvocationCallback invocation) throws Throwable {
//... 생략
if (txAttr == null || !(ptm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager)) {
TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(ptm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);
Object retVal;
try {
retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex);
throw ex;
}
finally {
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
//... 생략
commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo);
return retVal;
}
//... 생략
}
⒊ Case by Case attemptPasswordAuth에서 던진 AdminAccountPasswordNotMatchedException을 아래에서 잡아서 처리한다. 해당 메서드 내부의 주요 로직을 살펴보자. 중간에 rollbackOn이라는 메서드가 있다. DefaultTransactionAttribute 클래스를 보면 UncheckedException만 rollback 시킨다는 설명을 확인할 수 있다. 결국 AdminAccountPasswordNotMatchedException은 RuntimeException이기 때문에 Commit이 되지 않고, Rollback이 되는 것을 확인할 수 있었다. 추가적으로 위 메서드의 내부동작이 궁금하다면, AbstractPlatformTransactionManager 클래스의throw UncheckedException의 경우
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex);
protected void completeTransactionAfterThrowing(@Nullable TransactionInfo txInfo, Throwable ex) {
if (txInfo != null && txInfo.getTransactionStatus() != null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Completing transaction for [" + txInfo.getJoinpointIdentification() +
"] after exception: " + ex);
}
// 이부분!!!
if (txInfo.transactionAttribute != null && txInfo.transactionAttribute.rollbackOn(ex)) {
try {
txInfo.getTransactionManager().rollback(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
}
//... 생략
}
else {
//... 생략
}
}
}
txInfo.getTransactionManager().rollback(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
rollback(...), processRollback(...) 메서드를 보면 된다.
만약 코드를 아래와 같이 작성하면 rollback이 될까 commit이 될까? 애초에 내부에서 처리하였기 때문에 잡을 Exception이 없게 된다. 따라서 catch 부분은 통과하고 finally 부분 실행 이후 비록 Unchecked Exception이지만, 메서드 내부에서 예외처리를 해주면 Rollback이 되지 않고, Commit 됨을 확인할 수 있다.
try-catch Unchecked Exception의 경우
@Transactional
public void attemptPasswordAuth(String email, String inputPassword) {
if (!passwordEncoder.matches(inputPassword, account.getPassword())) {
try {
account.increaseLoginFailureCount();
adminAccountRepository.save(account);
throw new AdminAccountPasswordNotMatchedException();
} catch (AdminAccountPasswordNotMatchedException e) {
return;
}
}
// 이후 로직...
}
attemptPasswordAuth(...) 메서드에서 발생한 RuntimeException을 try-catch를 통해invocation.proceedWithInvocation() 실행이 되어도 catch에서commitTransactionAfterReturning() 메서드를 통해 커밋이 실행된다.
CheckedException의 경우에는 TransactionAspectSupport 클래스의 위에서 rollbackOn 메서드는 오로지 uncheckedException의 경우에만 롤백을 한다고 했다. 따라서 checkedException의 경우에는 else 조건절을 타게 되고, 해당 조건절에서 commit이 이루어진다.
throw CheckedException의 경우
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(...) 메서드를 파악하면 된다.protected void completeTransactionAfterThrowing(@Nullable TransactionInfo txInfo, Throwable ex) {
if (txInfo != null && txInfo.getTransactionStatus() != null) {
//... 생략
if (txInfo.transactionAttribute != null && txInfo.transactionAttribute.rollbackOn(ex)) {
try {
txInfo.getTransactionManager().rollback(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
}
//... 생략
}
else {
// !!!여기!!!
try {
txInfo.getTransactionManager().commit(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
}
//... 생략
}
}
}
txInfo.getTransactionManager().commit(txInfo.getTransactionStatus()) 메서드를 통해
문제점 정리
정리해보자면 최초에 작성한 코드의 문제는 아래와 같다.
- 비밀번호가 틀린 경우 AdminAccountPasswordNotMatchedException을 터트린다.
- AdminAccountPasswordNotMatchedException은 UnCheckedException이기에 롤백 된다.
- login_fail_count가 기대한대로 db에 업데이트가 안된다.
Solution1 - try/catch
위에서 정리한 대로 attemptPasswordAuth 메서드 내부에서 try-catch로 Exception을 처리하면 된다.
@Transactional
public void attemptPasswordAuth(String email, String inputPassword) {
if (!passwordEncoder.matches(inputPassword, account.getPassword())) {
try {
account.increaseLoginFailureCount();
adminAccountRepository.save(account);
throw new AdminAccountPasswordNotMatchedException();
} catch (AdminAccountPasswordNotMatchedException e) {
return;
}
}
// 이후 로직...
}
Solution2 - noRollbackFor
@Transactional은 보다 코드를 간략하게 작성할 수 있는 방식을 제공한다.
따라서 이번 문제의 해결책으로 @Transactional에서 제공해주는 noRollbackFor을 사용해보려한다.
코드는 정말 간단하다.
@Transactional(noRollbackFor = AdminAccountPasswordNotMatchedException.class) // <= 요기
public void attemptPasswordAuth(String email, String inputPassword) {
if (!passwordEncoder.matches(inputPassword, account.getPassword())) {
account.increaseLoginFailureCount();
adminAccountRepository.save(account);
throw new AdminAccountPasswordNotMatchedException();
}
// 이후 로직...
}
그러면 이제 내부 동작원리에 대해서 알아보자! ⒈ completeTransactionAfterThrowing 호출 ⒉ RuleBasedTransactionAttribute.java 참고 rollBackRules에 ⒊ 최초에 null이었던 winner에 NoRollbackRuleAttribute 할당 ⒋ false를 반환 3번에서 winner에 NoRollbackRuleAttribute 인스턴스가 할당됐기 때문에 false 반환. ⒌ 결과적으로 메서드를 통해 Commit이 이루어진다.noRollbackFor의 내부동작 이해하기
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex);
txInfo.transactionAttribute.rollbackOn(ex) 호출AdminAccountPasswordNotMatchedException이 있는 것을 확인할 수 있다.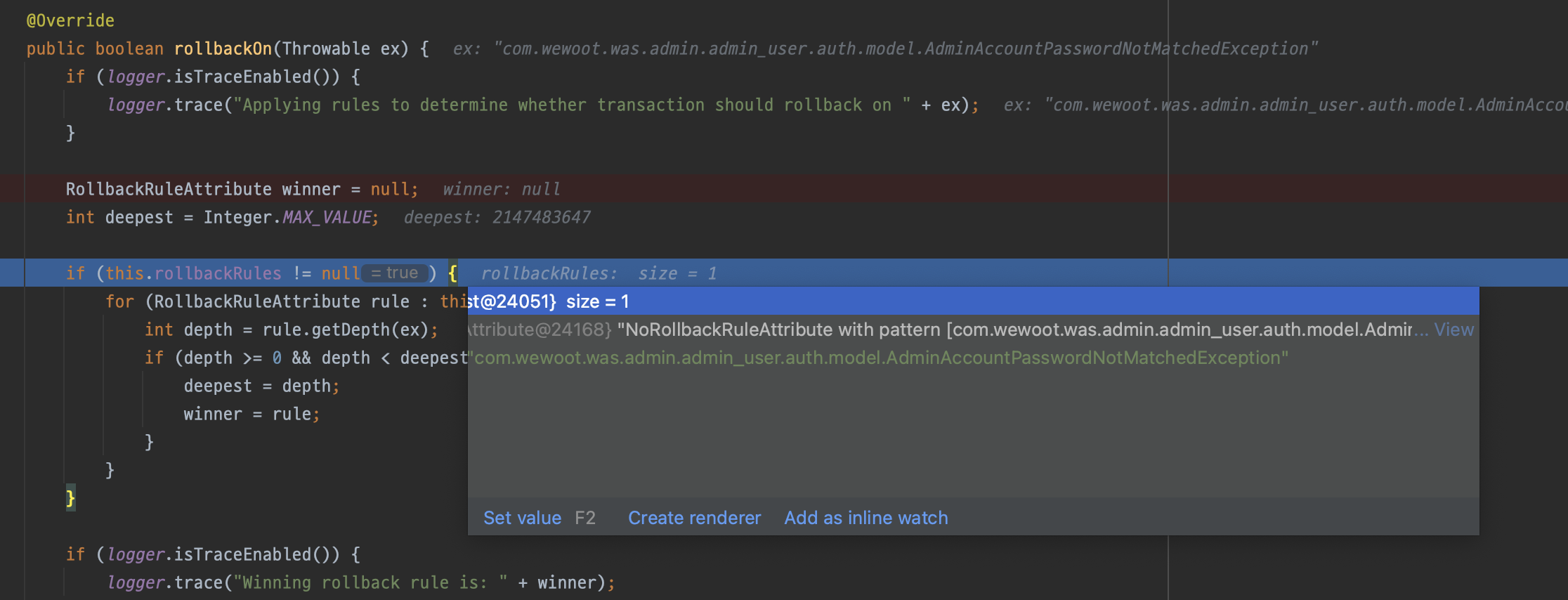
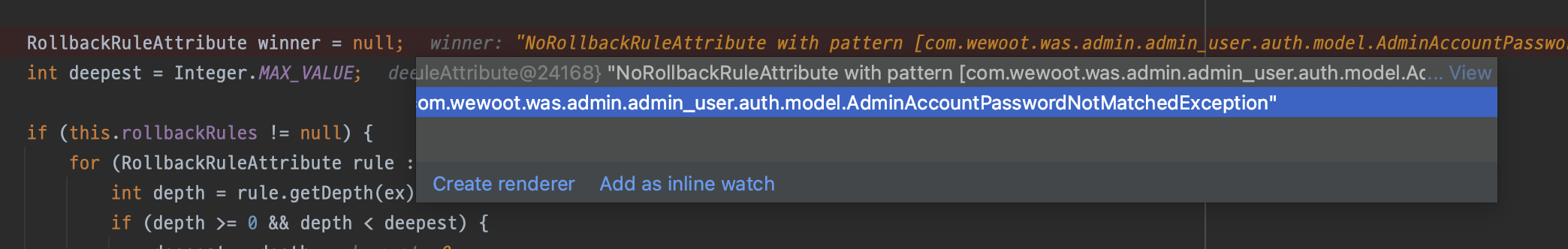
!(winner instanceof NoRollbackRuleAttribute);
TransactionAspectSupport.commitTransactionAfterReturning(...)protected void completeTransactionAfterThrowing(@Nullable TransactionInfo txInfo, Throwable ex) {
if (txInfo != null && txInfo.getTransactionStatus() != null) {
//... 생략
if (txInfo.transactionAttribute != null && txInfo.transactionAttribute.rollbackOn(ex)) {
try {
txInfo.getTransactionManager().rollback(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
}
//... 생략
}
else {
try {
txInfo.getTransactionManager().commit(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
}
//... 생략
}
}
}
txInfo.transactionAttribute.rollbackOn(ex) == false 이기 때문에 else 조건절을 탄다.txInfo.getTransactionManager().commit(txInfo.getTransactionStatus())
